Although the size of these cells is significantly smaller than the size of our body cells, their total weight still accounts for about 1.5-2 kilograms. Microorganisms can be found throughout the entire human body, however, they can be found in the largest quantity in the intestines, especially the large intestine. The mouth, the upper respiratory tracts, the genitals and the skin also have a significant quantity of microorganisms.
The reverberating success of microbiome research
Thanks to the latest molecular diagnostic procedures, our knowledge of the normal flora has been growing rapidly. Whilst only about 1% of the gut flora known today was identified with the traditional procedures, over 2000 species can be distinguished nowadays.
Thanks to the new, genomic-based procedures the diversity and the composition of the microbial communities can be specified accurately. It has been determined through large, population examinations that while about 30% of the microbiome is shared among the human race, about 70% of it is absolutely unique.
The role of the microbiome
The microbiome and the host have a close, bidirectional relationship with each other. There are plenty of essential microorganisms that are indispensable for the healthy functioning of the human body. Among these microorganisms we can find the bacteria responsible for the production of vitamins or the components of the gut flora that are responsible for keeping the balance of sugar metabolism by breaking down complex carbohydrates. At the same time, there are harmful bacteria as well that play a role in the development of certain diseases. We now know that, for example, the process of arteriosclerosis is also initiated by such bacterial metabolites produced by harmful microorganisms.
The close, bidirectional relationship of the microbiome and the host, as well as the large variability of the composition of the microbiome greatly contribute to the diversity, unique responsivity, sensitivity or disease predisposition of people. Based on the results of scientific research, the significance of the composition of microbiome is uncovered in the background of more and more physiological states and diseases.
In the background of which physiological states has the role of microbiome been proven?
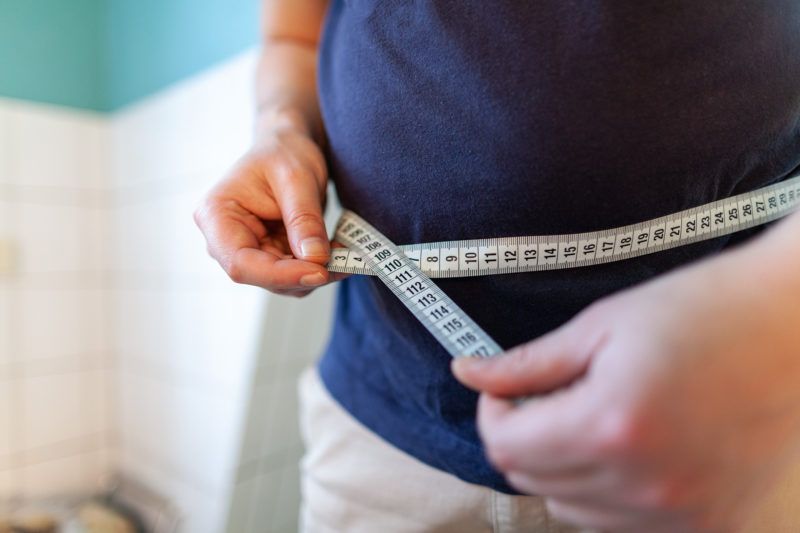
OBESITY
There is an ever-growing number of scientific evidence proving the role of microbiome in the development of obesity. Due to the excessive intake of calories, especially refined carbohydrates, and the lack of regular exercise, the composition of the gut flora changes (dysbiosis). In this case, such bacteria are produced by microorganisms in the intestines that spread by getting to different parts of the body via the circulatory system to obstruct the use of sugar and enhance the storage of energy, ultimately leading to the development of obesity, insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
DIGESTIVE DISORDERS
Many examinations justify the role of the changed microbiome in the background of digestive disorders (bloating, constipation, diarrhea, etc.). Numerous clinical examinations have proven the beneficial impact of probiotics, which support the theory that the recovery of the gut flora is important in order to terminate the symptoms.
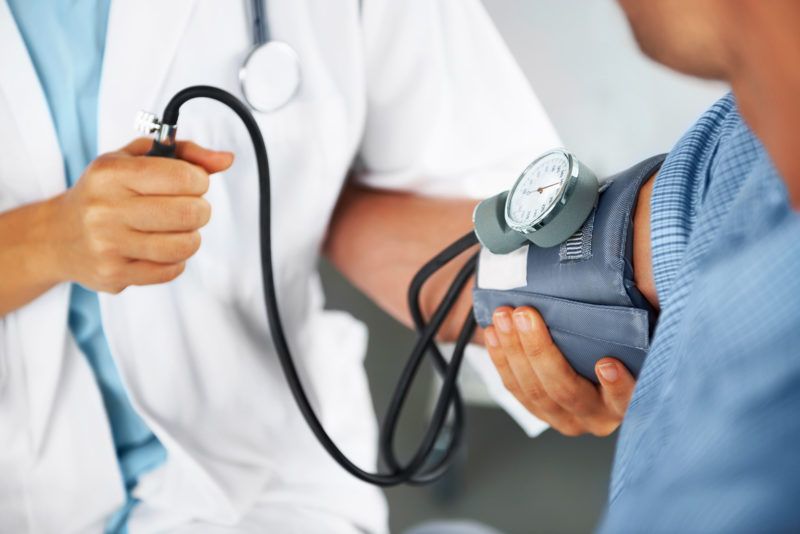
HYPERTENSION
Our hypothesis about the development of hypertension has been refined by the latest research results. That is because it has been proven that the gut flora changes due to the excessive intake of red meat and it starts producing such bacterial products that can be closely related to the development of arteriosclerosis and hypertension. The increased level of these bacterial products can be detected in the blood, which leads to the deposition of cholesterol in the blood vessels, arteriosclerosis and, ultimately, to the development of hypertension.
DIABETES
The so-called western-type diet (high intake of carbohydrates, within that, the high percentage of refined carbohydrates, excessive consumption of red meats, etc.), which is a characteristic feature of developed societies, fundamentally changes the composition of the gut flora as proven by several large clinical examinations. Bacteria are spread, which produce such bacterial products that, being absorbed, obstruct the development of insulin effect throughout the body, leading to insulin resistance or, ultimately, to type 2 diabetes.
How can I get a microbiome test?
1. Let us know your intention by getting in touch with us via the “Contact us” tab.
2. You will receive detailed information about the possibilities in connection with the microbiome examinations (contractual service provider, contractual doctor, private user).
3. You will receive the sampling kit.
4. The patient carries out the sampling at home and takes the sample to the healthcare service provider.
5. We receive the samples, process them and evaluate the results.
6. We prepare a detailed analysis about the results, which the doctor then cross-checks with the patient during a consultation.
To get a microbiome test, call us on +36 70 905 30 80 or write an email to info@mind.hu.
With this video, we would like to provide practical help for the sampling. Our colleague lets you know about all the deatils, shows you how to use the kit correctly and draws the attention to the possible mistakes during the sampling as well.