Ultrasound is a widely used diagnostic technique because it causes no discomfort or risk to the patient. It works with sound waves and does not involve any radiation exposure. It is a basic examination, often the first imaging method that physicians employ. Various tissues in the body conduct ultrasound well, allowing evaluation of many organs (except bones and the lungs). Ultrasound is typically used to examine the neck vessels as well as abdominal and pelvic organs.
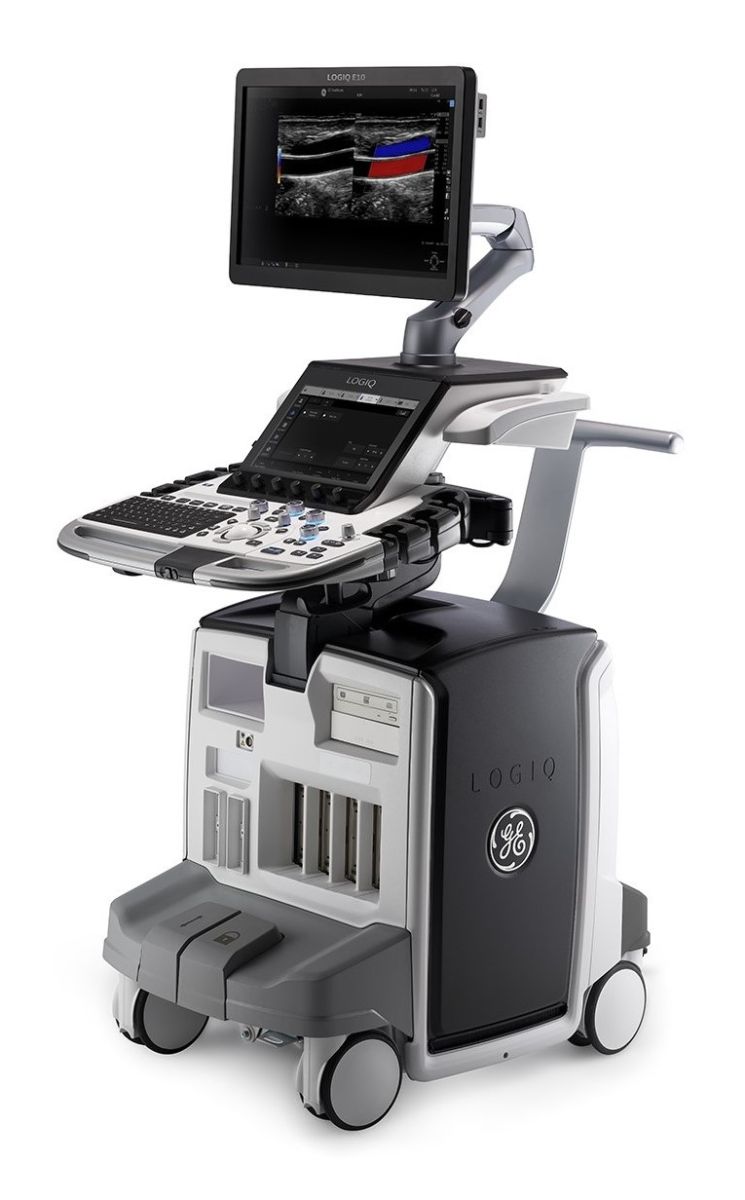
Our state-of-the-art ultrasound system (GE LogiQ E10) offers extensive technical and software capabilities, along with a comprehensive set of transducers, enabling a wide range of diagnostic examinations. This machine takes reliability and effective diagnostics to a whole new level by incorporating artificial intelligence during examinations. As a result, image optimization requires fewer steps, allowing physicians to dedicate more time to the patient.
ULTRASOUND EXAMINATIONS PERFORMED AT MIND CLINIC
- Comprehensive abdominal and pelvic ultrasound
- Liver elastography
- Examination of venous circulation in the lower (and occasionally upper) limbs
- Large joint ultrasound (shoulder, hip, knee) for adults
- Pediatric abdominal and pelvic ultrasound
- Newborn hip joint ultrasound
- Carotid Doppler
- Neck soft tissue ultrasound (thyroid)
IMPORTANT INFORMATION BEFORE THE EXAMINATION
Please note that some preparations are necessary for certain examinations to be performed successfully.
For abdominal ultrasound: You need to arrive with a 6-hour fast and a full bladder. To achieve this, go to the restroom 2 hours before your appointment, then drink 2 large glasses of water (approximately 0.5 liters) and refrain from using the restroom until the examination is completed.
For Fibroscan examination: A 6-hour fast is required before the test. This means you should not eat or drink anything during the 6 hours prior to your appointment. If your appointment is in the afternoon, try to eat a lighter meal in the morning with minimal animal protein and fat.
If both abdominal ultrasound and Fibroscan are scheduled together: Maintain the 6-hour fast (no food or drink), and do not empty your bladder during the 3–4 hours before the examination.
When both abdominal ultrasound and Fibroscan are performed at the same time, the Fibroscan preparation instructions take precedence.
FURTHER INFORMATION REGARDING ULTRASOUND EXAMINATION
DETAILED DESCRIPTION OF INDIVIDUAL ULTRASOUND EXAMINATIONS
Abdominal and Pelvic Ultrasound (Overview)
This examination includes a detailed assessment of the liver and bile ducts, as well as the pancreas, spleen, adrenal glands, kidneys, urinary bladder, internal reproductive organs, major abdominal vessels and their surroundings, and evaluation of lymph node status. Due to the method's sensitivity, it effectively detects diffuse or focal liver abnormalities, gallstones or inflammatory bile duct diseases, and, in favorable cases, identifies causes of bile flow obstruction. Changes in the pancreas (mainly head and body), splenomegaly, structural abnormalities of the spleen, and, if applicable, signs associated with hematologic disorders (enlarged lymph nodes) can also be observed. The right adrenal gland’s focal lesions (adenoma, metastasis) are almost always visible, while the left adrenal gland is less well depicted due to its anatomical position. Detailed bilateral kidney examination identifies congenital (e.g., cysts) or acquired (e.g., tumors) abnormalities, primarily urological issues (stones, drainage problems), and evaluates internal medicine-related kidney conditions (based on parenchymal thickness and ultrasound reflection characteristics). Within the modality’s limitations, gastrointestinal complaints, bowel wall abnormalities, or passage disorders (e.g., signs of inflammatory bowel disease or strictures) are assessed. Pleural sinus areas are examined for possible pleural fluid, and inguinal regions may be evaluated for enlarged lymph nodes or hernias. In the pelvis, prostate size and relation to the bladder base are assessed in men; in women, the uterus’ size, shape, and position (ante- or retroflexion) are described, and ovaries are evaluated if the bladder is adequately filled.
Lower (or Upper) Limb Venous Doppler
The venous circulation of the lower (and occasionally upper) limbs is examined to detect thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, venous valve insufficiency, or varicose veins. Direct compression, color Doppler, and duplex studies are performed during vascular limb assessment.
Large Joint Ultrasound for Adults
For orthopedic evaluation, large joint ultrasound (shoulder, hip, knee) is performed. This assesses superficial joint soft tissues (ligaments, tendons, visible cartilage), evaluates bursae (fluid detection and synovial status), and examines surrounding muscles and tendons. The examination effectively detects degenerative, inflammatory, or traumatic changes, and can evaluate post-injury muscle or tendon lesions (partial or complete tears) and common painless subcutaneous lesions (lipomas, fibrolipomas).
Pediatric Abdominal and Pelvic Ultrasound
Performed for children aged 0–18, both as a screening in asymptomatic cases and for abdominal complaints. Screening focuses on detecting developmental or other kidney and urinary tract abnormalities, and excludes rare early malignant kidney or adrenal processes. For newborns and infants up to 2 years old, fasting is not required.
Newborn Hip Ultrasound
This screening examines signs of hip developmental disorders (hypoplasia, dysplasia) in newborns and follows up based on findings.
Carotid Doppler
Examines the main neck arteries, mainly for atherosclerosis and stroke risk. Plaque formation (from fat, cholesterol, calcium, or other substances) can narrow the carotid arteries. Early diagnosis and treatment of stenosis significantly reduce stroke risk. Assessment includes arterial course, wall thickening, plaques, and flow studies to detect stenosis. Common indications include headache, high blood lipids, and hypertension.
Elastography
This advanced ultrasound technique (elastography, fibroscan, elastoscan) measures tissue stiffness, providing additional information beyond standard ultrasound. Different tissue stiffness is displayed in colors on the monitor (e.g., thyroid, liver), allowing early detection of minor abnormalities. Indications include liver disease assessment (fat content, fibrosis, tissue remodeling), and precise diagnosis and monitoring of liver conditions of unknown origin.
Neck Ultrasound
Assesses superficial neck abnormalities, muscles, lymph nodes, thyroid size and structure (nodules, thyroiditis), salivary glands, stones, inflammations, and benign or malignant tumors. Common indications include palpable neck lumps, sensation of a lump, firm neck, abnormal thyroid lab values, swallowing discomfort, or painful/inflamed salivary glands.
Dr. Bács Éva
Radiologist

Dr. Gelley András
Gastroenterologist, Internist

Dr. Réda Bea
Radiologist